Cyber Resilience in Healthcare: Securing Lifesaving Infrastructure in a Digital Age
Blog / 4 min read / Saurav Singh

The healthcare industry forms the backbone of national well-being, delivering essential care and emergency services every day. This blog post discusses the multiple advantages of using an integrated cybersecurity solution, as well as its effectiveness in combating changing cyber threats.
As hospitals adopt automation, digital medical devices, and connected infrastructure, their Operational Technology systems, such as HVAC in ICUs, oxygen supply controls, and medical imaging equipment, have become vital and vulnerable. With increasing connectivity comes increased risk.
Cyberattacks targeting hospitals, diagnostic centers, and pharmaceutical supply chains are rising sharply, with threat actors exploiting both legacy equipment and weak remote access points. The result: patient safety, hospital operations, and public trust are at stake.
Recent High-Profile Incidents Underscore the Growing Risks
Universal Health Services (UHS) Attack (2020):
Universal Health Services (UHS), a large U.S. hospital chain, suffered a massive cyberattack over the weekend, likely a ransomware attack. This caused widespread system failures, forcing hospitals to revert to manual processes for patient information. The attack disrupted critical hospital operations, including medication management, and delayed patient care. Experts warn such incidents can be life-threatening, as delays in treatment and rerouting patients can have serious consequences. This highlights the growing cybersecurity risks in the healthcare sector.
AIIMS Delhi Ransomware Attack (2022):
In December 2022, the All-India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) in New Delhi experienced a ransomware attack, resulting in the encryption of 1.3 terabytes of data and affecting five servers. The attack caused major disruptions to the institute's operations for nearly two weeks. The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) evaluated the incident, and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology confirmed that AIIMS managed its own IT systems. The government has advised remedial measures to address the cybersecurity breach.
India Malware Attack Surge (2024): Healthcare and Hospitality Among Top Targets
India faced 370 million malware attacks in 2024, with sectors like healthcare (22%) and hospitality (20%) being the most targeted. Key findings include over one million ransomware detections and significant threats to sectors like BFSI, education, and MSMEs. Trojan malware was the most common, accounting for 43% of the attacks. Regions like Telangana, Tamil Nadu, and Bengaluru were hotspots.
Kettering Health Hit by Interlock Ransomware Attack (2025)
A ransomware attack at Kettering Health, a major Ohio medical network, caused a system-wide outage, disrupting 14 centers and canceling elective procedures. Emergency services remain open, but the network is working to recover. The attackers threatened to leak stolen data unless a ransom is paid. The FBI and other agencies are investigating. This attack underscores the increasing vulnerability of U.S. healthcare to cybercrime, with over 440 ransomware incidents reported in 2024.
Key Threats to Healthcare OT Systems
- Ransomware & Extortion
Attackers target hospital control systems, imaging networks, and BMS, encrypting them or stealing sensitive records to demand ransom.
- Medical Device Exploitation
Equipment like infusion pumps, ventilators, CT scanners, and dialysis machines often runs outdated software. These devices lack encryption and are not regularly monitored, making them easy targets.
- BMS (Building Management System) Vulnerabilities
Critical hospital systems like oxygen delivery, HVAC, power management, and fire suppression are controlled digitally. A breach could shut down life-support systems or create unsafe environmental conditions.
- IoMT & Remote Access Risks
As hospitals adopt remote diagnostics and connected monitoring systems, insecure VPNs or exposed ports become entry points for attackers.
- Legacy OT Devices
Many hospital OT systems, including control panels, PLCs, and UPS systems, are decades old and cannot be easily patched or secured.
- Insider Threats & Third-Party Risks
Technicians, vendors, and contractors with privileged access can introduce vulnerabilities, either unintentionally or maliciously.
Impacts of Cyberattacks on Healthcare OT Networks
- Patient Safety Threats: Life-support systems, ICU controls, or imaging machines going offline can lead to delayed or denied care.
- Operational Downtime: Ransomware can halt lab operations, delay surgeries, or cripple emergency responses.
- Regulatory and Legal Exposure: Breaches of patient data lead to non-compliance with data protection laws like HIPAA, GDPR, or India’s DPDP Act.
- Financial Losses: Hospitals face costs from incident response, canceled procedures, system replacement, and potential lawsuits.
- Reputation Damage: Public trust in healthcare institutions declines after visible disruptions or data leaks.
Defending Healthcare OT Infrastructure: Best Practices
- Network Segmentation
Separate OT networks from IT systems using firewalls, VLANs, and secure zones. Limit access between administrative systems and clinical control infrastructure.
- Role-Based Access & MFA
Control access using strict user roles and enforce multi-factor authentication, especially for vendors and remote technicians.
- Patch & Virtual Patching
Apply security patches to devices where possible. For legacy systems, implement virtual patching and enforce strict external filtering to protect unpatchable devices.
- OT-Specific Monitoring
Deploy monitoring systems that detect unusual activity within medical protocols and hospital automation systems such as Modbus, BACnet, and DICOM.
- Secure Remote Access
Use jump servers, encrypted VPNs, and time-based access controls. All vendor access should be logged and monitored in real time.
- Incident Response Planning
Create response playbooks for ransomware, system lockouts, or patient care disruptions. Include escalation, communication, and manual fallback procedures.
- Employee Awareness & Training
Educate hospital and engineering staff on safe device usage, phishing prevention, and cyber hygiene. Include technicians who handle OT systems.
- Offline & Immutable Backups
Store regular backups of system configurations, device firmware, and patient data offline. Protect them from tampering and test recovery protocols frequently.
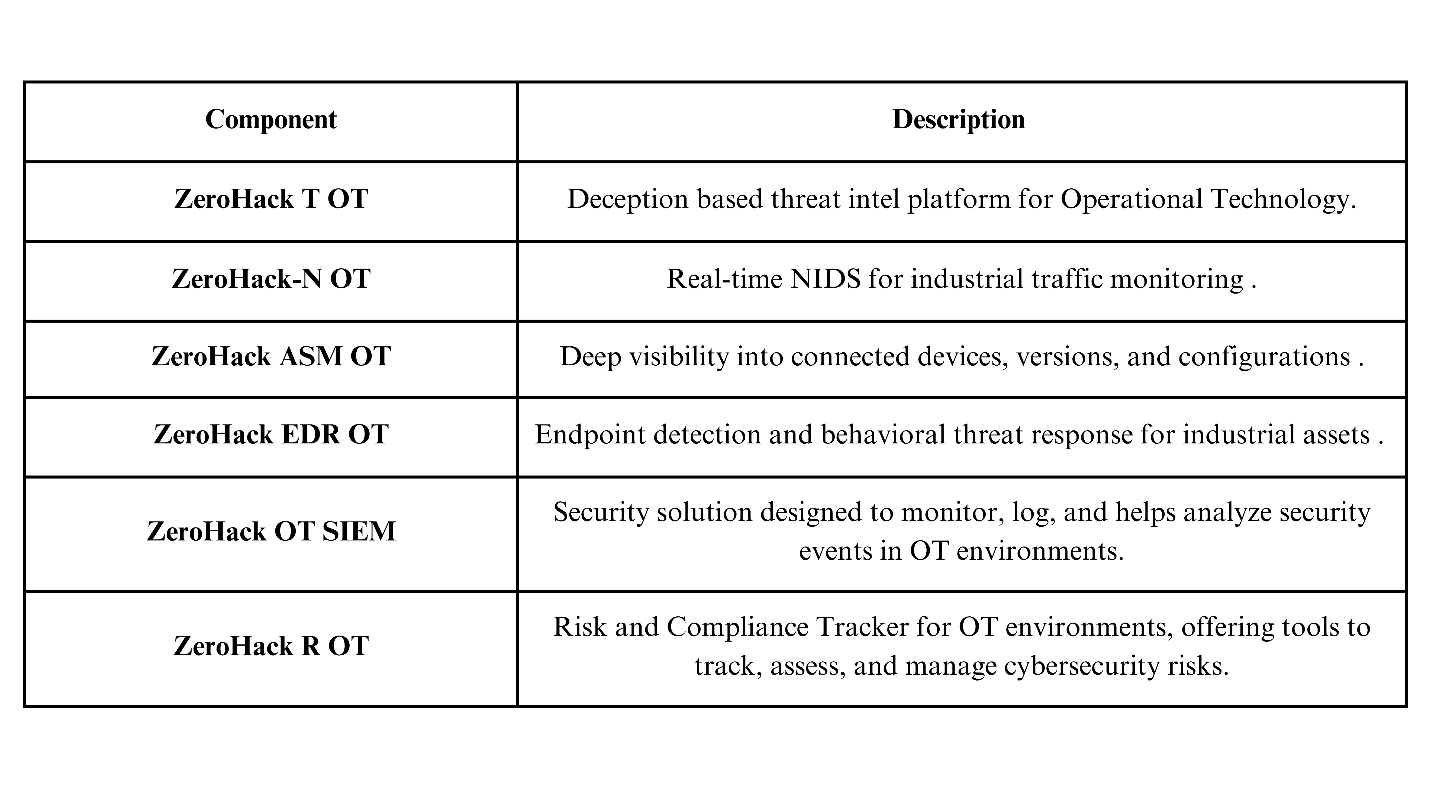
So, to overcome this, we have India’s First Complete OT Security Portfolio - Now Tailored for Healthcare
WhizHack Technologies introduces the country’s first built OT cybersecurity platform for the healthcare sector.
Let’s Start the Conversation
- Are your imaging machines, BMS, and pharmacy automation systems properly segmented from your administrative network?
- Have you tested your hospital’s recovery capability after a ransomware attack on critical OT systems?
- Have you deployed decoy services to detect and study early-stage cyber threats?
- Are your OT backups protected, tested, and ready for emergency restoration?
Reach out to WhizHack Technologies today and schedule your OT Security Consultation. Together, let’s secure healthcare industries.