Operational Technology (OT) Cybersecurity: A Rising Threat to the Manufacturing Sector
Blog / 4 min read / Saurav Singh

In today's world, manufacturing facilities drive global economies, powering industries that range from consumer goods to critical machinery. As automation and smart technologies become more prevalent, however, the Operational Technology (OT) systems that control these vital processes are increasingly becoming targets for cybercriminals. The surge in cyberattacks on manufacturing systems emphasizes the critical need for robust OT cybersecurity measures to protect operations from catastrophic disruption. This blog post discusses the multiple advantages of using an integrated cybersecurity solution, as well as its effectiveness in combating changing cyber threats.
Recent high-profile cyberattacks in the manufacturing sector illustrate the growing risks:
- In 2024, the manufacturing sector was the most targeted by ransomware attacks, followed by professional and technical services, together making up 40% of incidents, according to Arete’s Annual Crimeware Report. Despite a steady median ransom demand of $500,000, only 29% of victims paid, down from 32% in 2023. Most attacks were opportunistic, not industry specific. Organizations increasingly adopted security measures like EDR and MFA. Key ransomware groups included Akira, RansomHub, Play, Qilin, and Lynx, who based demands on financial data stolen during attacks.
- Manufacturing remains the most targeted industry by cybercriminals for the third consecutive year, according to IBM's X-Force Threat Intelligence Report. The sector’s low tolerance for downtime makes it an attractive target, with over 25% of security incidents last year involving manufacturers—mostly through ransomware and credential harvesting. A staggering 85% of attacks on critical infrastructure could have been prevented with basic security measures like patching, MFA, and least-privilege access. Additionally, 42% of U.S. cyberattacks stemmed from criminals using valid credentials, highlighting poor access control. The report stresses that as threats evolve especially with the use of AI by cybercriminals—manufacturers must adopt stronger cybersecurity practices, such as stress-testing systems, implementing MFA, and using AI-based behavioral analytics to detect identity-based threats.
- A global study by Omdia found that 80% of manufacturers faced more cyberattacks last year, but only 45% were prepared. Cyberattacks cost firms $200,000 to $2 million, especially when affecting production systems. The report highlights the need for stronger cybersecurity as manufacturers adopt IT and OT technologies like cloud, AI, and IoT.
- India ranks second in the Asia Pacific region for ransomware attacks, with the manufacturing sector being the hardest hit, accounting for 28.89% of incidents. Other vulnerable sectors include healthcare, financial services, technology, and pharmaceuticals.
Key Threats to Manufacturing OT Systems
-
Ransomware Attacks:
Cybercriminal groups, such as the ones behind the Honda attack, often deploy ransomware to lock down manufacturing systems, demanding a ransom for the release of critical data or to restore access to systems. The downtime caused by such attacks can halt production lines for days or even weeks. -
SCADA System Exploitation: SCADA systems used to control manufacturing processes are attractive targets. Cyber attackers can manipulate or take control of SCADA systems to disrupt production processes, change machine settings, or trigger malfunctions. This can result in downtime, production errors, or even permanent damage to critical manufacturing equipment.
-
Remote Access Vulnerabilities: Manufacturing plants often use remote access tools to manage systems and equipment across locations. Weaknesses in VPNs, RDP, or exposed ports provide hackers with unauthorized access to OT environments. This access allows them to steal sensitive data or manipulate systems, disrupting manufacturing operations.
-
Legacy Devices: Many manufacturing facilities still rely on outdated devices such as PLCs, HMIs, and other industrial control systems that lack modern security features. These legacy devices often cannot be patched, creating significant vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
-
Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to critical systems can intentionally or unintentionally introduce malware, steal data, or tamper with controls, resulting in severe disruptions. Insider threats are particularly difficult to defend against, as these individuals often have trusted access to critical systems.
Impacts of Cyberattacks on Manufacturing
-
Production Downtime: Cyberattacks can cause significant downtime, halting entire production lines. The longer the downtime, the greater the financial losses and customer dissatisfaction, as companies struggle to meet production schedules and fulfill orders.
-
Financial Losses: The cost of a cyberattack extends beyond immediate operational disruptions. Manufacturers may face hefty ransom demands, penalties for non-compliance with cybersecurity regulations, and potential loss of business due to diminished customer trust.
-
Equipment Damage: Malicious cyberattacks can result in equipment failure by altering machine parameters or damaging production machinery. This can lead to costly repairs or the need for complete replacements, disrupting production timelines and causing financial strain.
-
Intellectual Property Theft: Cybercriminals can also target sensitive intellectual property such as product designs, patents, or manufacturing processes. The theft of intellectual property can lead to loss of competitive advantage, affecting market positioning and profitability.
-
Regulatory Penalties and Legal Risks: Cyberattacks that lead to data breaches or operational disruptions can result in regulatory penalties. Non-compliance with industry-specific cybersecurity standards, such as NIST or ISO 27001, can also expose manufacturing companies to lawsuits and fines.
Best Practices to Defend Manufacturing OT Systems
-
Network Segmentation: Segment OT networks from IT networks and external internet connections to limit the spread of any potential cyberattack. Implement firewalls, DMZs, and VLANs to isolate critical manufacturing systems.
-
Access Control & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforce strict access controls for OT environments and require multi-factor authentication for all remote connections. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and helps prevent cyberattacks that target remote access vulnerabilities.
-
Patch Management: Regularly update software and firmware on OT systems wherever possible. For legacy devices that cannot be patched, deploy compensating security controls such as virtual patching or intrusion detection systems.
-
Intrusion Detection & Monitoring: Implement OT-specific intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor for abnormal activities or system anomalies that could indicate a cyberattack.
-
Secure Remote Access: Use encrypted VPNs, jump servers, and session recording to secure remote access to OT systems. Restrict access to defined time windows and ensure all remote access is logged and monitored for suspicious activity.
-
Incident Response Plans: Develop, test, and refine incident response plans to ensure that in the event of an attack, the response is swift, organized, and effective. Include contingencies for ransomware attacks, manufacturing system failures, and SCADA compromises.
-
Employee Training: Regularly train employees, operators, and engineers on cybersecurity best practices, including recognizing phishing attacks, safely using USB devices, and following safe practices when working with OT systems.
-
Offline Backups: Maintain offline, secure backups of critical data, configuration files, and control logic to ensure that production systems can be restored quickly in the event of an attack.
With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting manufacturing facilities, investing in a comprehensive OT security strategy is no longer optional. It’s essential.
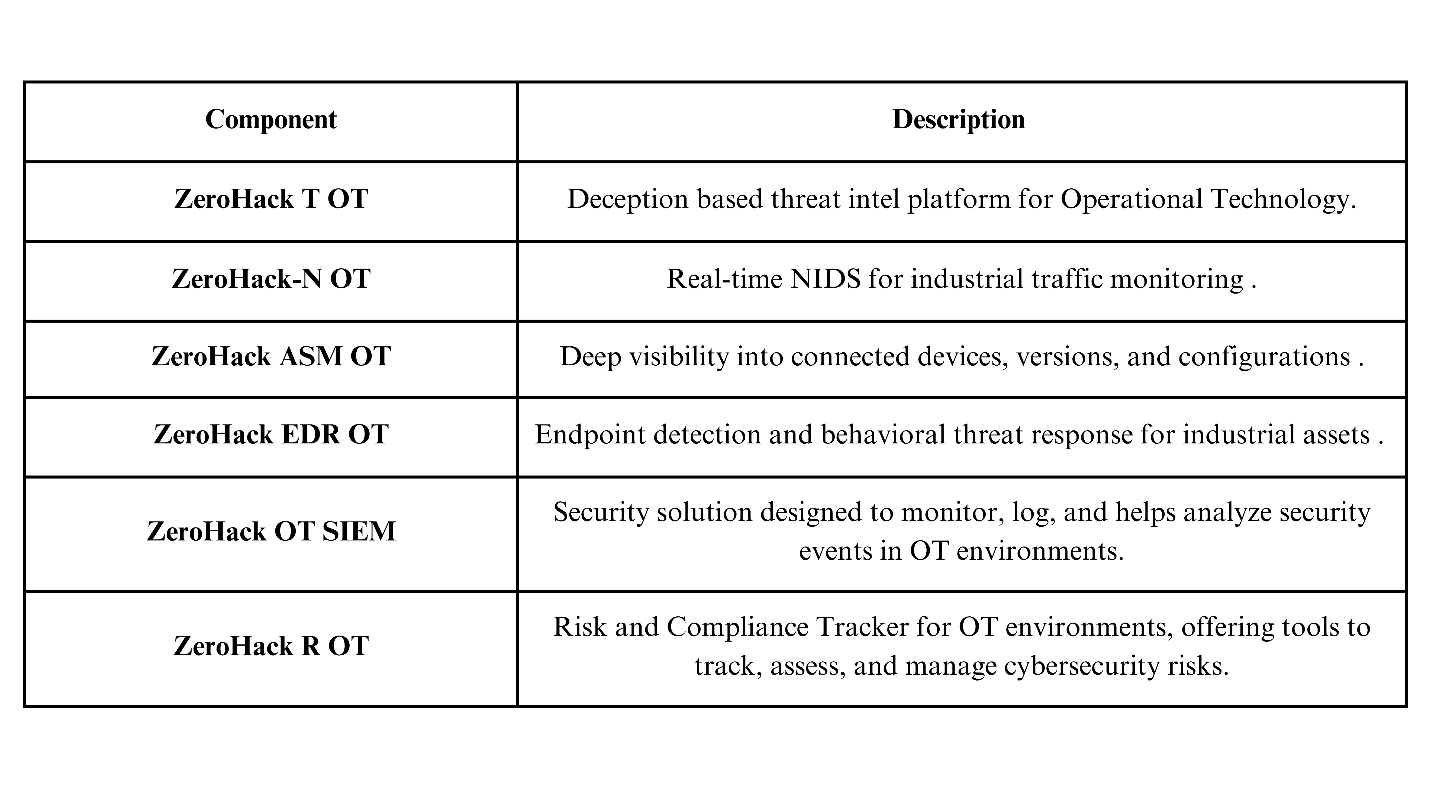
To overcome this, presenting you India’s first complete OT security portfolio – built for manufacturing sector, precision & resilience:
Let’s Start the Conversation
- Is your manufacturing OT environment segmented from your IT network with robust firewalls and access control policies?
- How resilient are your legacy systems to modern cyber threats?
- Can your production lines quickly recover from a ransomware attack?
Reach out to WhizHack Technologies today and schedule your OT Security Consultation. Together, we can safeguard your manufacturing operations and ensure resilience in an increasingly connected world.