The Oil & Gas industry is the backbone of global energy supply, powering homes, transportation, and industries. With increasing digitalization, automation, and remote operations, Operational Technology (OT) systems that control exploration, extraction, refining, and distribution are becoming high-value targets for cybercriminals. This blog post discusses the multiple advantages of using an integrated cybersecurity solution, as well as its effectiveness in combating changing cyber threats.
Recent high-profile cyberattacks in the oil and gas sector illustrate the growing risks:

On August 22, 2024, oil giant Halliburton reported a system issue widely believed to be caused by a cyberattack, potentially affecting operations at its** Houston campus and international networks.** While Halliburton did not confirm the cyberattack, it activated its response plan and is investigating the issue with cybersecurity experts. The U.S. Department of Energy stated there was no evidence of disruption to national energy services. This incident highlights growing cybersecurity risks for companies managing critical infrastructure, following similar high-profile attacks in recent years.
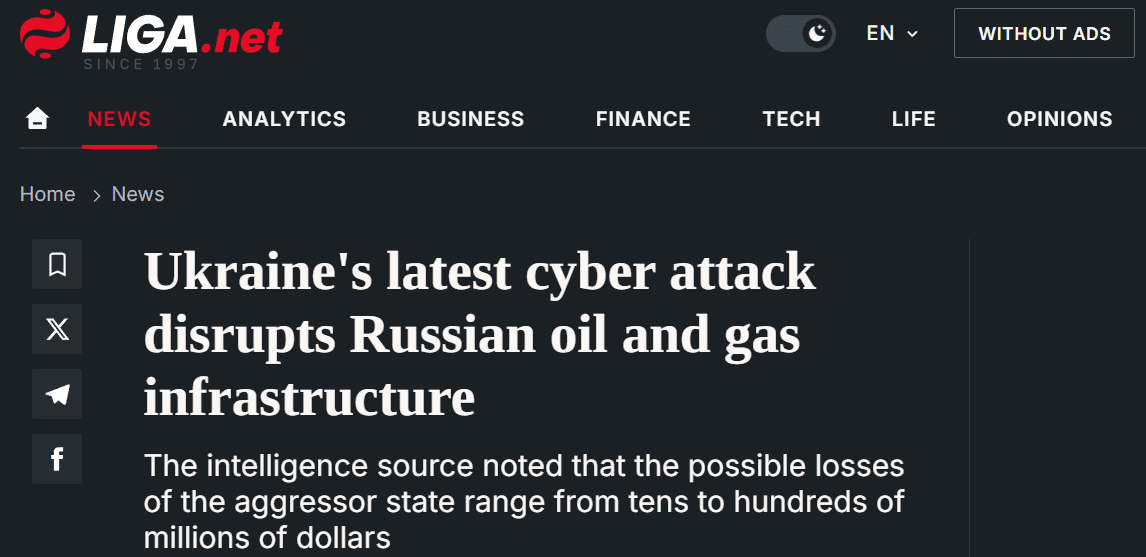
In February 2025, Ukrainian cyber forces launched a major attack on over 23 Russian oil and gas companies, including Gazprom’s contractor Gazstroyprom. The operation disabled servers, destroyed 2,000 TB of data, and shut down over 10,000 computers, causing losses estimated in the tens to hundreds of millions of dollars. This was part of a broader cyber campaign targeting Russia’s energy sector.
In May 2021, Colonial Pipeline, one of the largest fuel pipelines in the U.S., was forced to shut down its 5,500-mile system due to a ransomware attack, severely disrupting fuel supply across the East Coast. The attack, attributed to a** criminal hacking group**, targeted Colonial’s corporate IT systems, prompting the company to halt operations as a precaution. The pipeline, which transports 2.5 million barrels of fuel daily, supplies about 45% of the East Coast's fuel. While the full impact on prices was initially limited, the incident exposed significant cybersecurity vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure and prompted federal investigations and calls for stronger national cyber defenses.
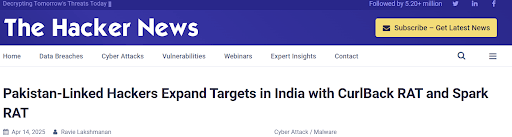
A Pakistan-linked hacking group tied to APT36 and SideCopy has expanded attacks on Indian sectors like railways, oil and gas, and foreign affairs. They now use MSI files instead of HTA for malware delivery, spreading new tools such as CurlBack RAT (Windows) and Spark RAT (cross-platform) through phishing emails containing fake documents. The group uses advanced techniques like DLL side-loading and PowerShell-based decryption, aiming to steal data, execute commands, and avoid detection—showing increasing sophistication in their cyber operations. (https://thehackernews.com/2025/04/pakistan-linked-hackers-expand-targets.html)
So here are some key threats to oil & gas OT Systems
- Ransomware & Extortion: - Attackers increasingly target OT systems to encrypt control processes or exfiltrate sensitive engineering data. Ransom demands are often based on stolen financial and operational information.
- SCADA & DCS Exploitation: - Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS) are widely used in Oil & Gas. These systems, if breached, can allow attackers to halt drilling, disrupt refining, or create unsafe pressure levels in pipelines.
- Remote Asset Exploitation: - Offshore platforms, remote well sites, and distributed pipeline infrastructure rely on satellite and VPN-based remote access. Weak credentials and exposed ports leave these systems vulnerable to attack.
- Legacy ICS Devices: - Much of the energy sector relies on decades-old control equipment, often running outdated software. These devices cannot be easily patched and lack basic protections like encryption or access logging.
- Insider Threats & Third-Party Risks: - Contractors, vendors, and internal personnel with deep system access pose a significant risk. Misuse intentional or accidental can disrupt operations or provide footholds for external attackers.
Impacts of Cyberattacks on Oil & Gas Network
- Production Downtime: - Attacks can halt drilling, refining, or pipeline distribution causing millions in daily losses and impacting fuel supply chains worldwide.
- Environmental & Safety Risks: - Compromised OT systems could result in oil spills, gas leaks, or fires posing dangers to personnel, communities, and ecosystems.
- Financial & Reputational Damage: - Beyond ransom costs, firms may face environmental penalties, regulatory scrutiny, and damaged trust from customers, partners, and investors.
- Loss of Intellectual Property: - Cyberattacks often aim to steal sensitive data such as drilling plans, geological data, or proprietary chemical formulations.
- Geopolitical Tensions: - Oil & Gas infrastructure is a frequent target in nation-state cyber warfare. Attacks can disrupt national energy supply and raise geopolitical risks.
Defending Oil & Gas OT Infrastructure: Best Practices
- Network Segmentation: - Isolate OT systems from IT networks and external connections using firewalls, DMZs, and ICS-specific segmentation strategies.
- Zero Trust & MFA: - Implement a Zero Trust approach with identity-based access controls and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all remote and privileged users.
- Patch & Vulnerability Management: - Prioritize patching of internet-facing systems and apply compensating controls (e.g., virtual patching) where legacy systems cannot be updated.
- OT-specific Threat Detection: - Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools tailored for ICS environments.
- Secure Remote Access: - Employ jump servers, encrypted VPNs, session recording, and time-based access controls to secure connections to remote assets.
- Incident Response & Crisis Planning: - Develop incident response protocols specific to Oil & Gas scenarios, including shutdown sequences, system failovers, and emergency drills.
- Training & Awareness: - Educate engineers, control room staff, and field operators on OT security hygiene phishing, USB policies, and safe use of HMI interfaces.
- Offline & Immutable Backups: - Ensure that all control configurations, process data, and critical software are backed up offline and protected from tampering.
The Oil & Gas industry must prioritize OT cybersecurity. In an environment where downtime equals disaster, resilience is not a luxury, it’s a necessity.
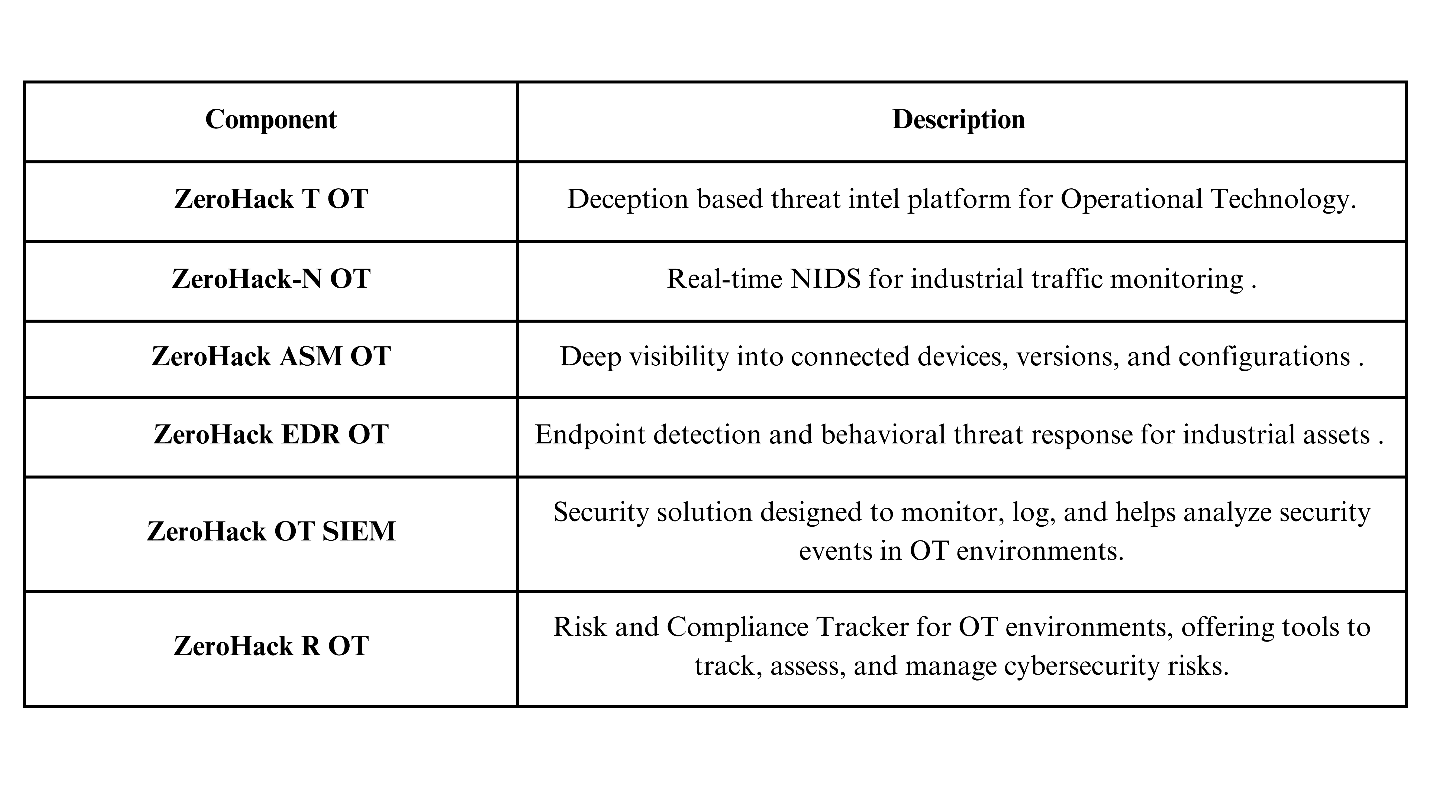
India’s First Complete OT Security Portfolio—Now Tailored for Oil & Gas
WhizHack Technologies proudly introduces its dedicated OT security solutions for the Oil & Gas sector ensuring operational resilience, regulatory compliance, and safety.
Let’s Start the Conversation
- Have you conducted any Ransomware simulation tests to assess possible vulnerabilities in your network?
- Have your employees and key officials been trained and certified on potential OT security breaches?
- Is your OT network especially SCADA and DCS systems segmented and protected from external IT networks and the internet?
- Is your OT network especially SCADA and DCS systems segmented and protected from external IT networks and the internet?
- How secure is remote access to your offshore platforms, pipeline control centers, and unmanned facilities?
- Do you have tested incident response and recovery plans specific to OT systems, including shutdown and failover procedures?
Schedule your OT Security Consultation with WhizHack today. Together, we can secure India’s energy backbone and build a cyber-resilient Oil & Gas ecosystem.