Operational Technology (OT) has become the backbone of modern infrastructure powering everything from factories and hospitals to smart campuses and city grids. This blog post discusses the multiple advantages of using an integrated cybersecurity solution, as well as its effectiveness in combating changing cyber threats.
But as the convergence between IT and OT grows deeper, these once-isolated systems are now prime targets for cyberattacks.
The 2025 OT Security Reality Check :
- 75% of OT systems will be internet-connected by 2025.
- 70% still use legacy tech without built-in security.
- Over 90% of OT-using organizations have suffered a breach in the last two years.
- The OT security market is expected to hit $25 billion by the end of 2025.
OT Security Challenges (2025)
Despite increased awareness, OT environments continue to struggle with:
- Legacy Infrastructure: Outdated systems with no patching support
- IT-OT Convergence Risks: Increased attack surface through integration
- Shortage of OT Security Experts
- Blind Spots: Lack of visibility and real-time monitoring
- Limited Incident Response Readiness in OT teams
Sector-Wise Threats, Detailed Impacts & Solutions
1. Manufacturing
Key Threats:
- Ransomware
- Supply chain injection
- Malicious reprogramming of PLCs
Real Attack: Tata Power (India, 2022): Cyberattack disrupted operations and leaked sensitive data.
Detailed Impact:
- Incident: In October 2022, Tata Power was targeted by the Hive ransomware group.
- Attack Method: The group used double-extortion tactics encrypting data and threatening to leak sensitive information unless a ransom was paid.
- Data Leaked: Personal details of employees, technical drawings, financial records, and customer information were compromised.
- Vulnerabilities Exploited: The attackers exploited an outdated, unpatched Boa web server, which was discontinued in 2005 but still in use.
- Impact on Operations: While operational systems were not affected, the breach revealed weaknesses in Tata Power’s IT infrastructure.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: The attack highlighted the potential risks to critical infrastructure in India, especially with growing digital interconnectedness.
Solutions:
- ZeroHack EDR OT – Endpoint protection for PLCs and HMIs
- ZeroHack Asset Management OT – Maps all devices, finding vulnerability in systems
- WhizRange – Train engineers in breach scenarios via realistic simulation
2. Energy & Utilities
Key Threats:
- State-sponsored attacks
- Remote access exploitation
- SCADA network manipulation
Real Attack:
Colonial Pipeline (USA, 2021): Ransomware crippled fuel distribution, causing nationwide panic.
Detailed Impact:
- Operational Disruption: The attack led to a six-day shutdown of Colonial Pipeline's operations, affecting the distribution of gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel across the U.S. East Coast. CISA
- Fuel Shortages: The disruption caused localized fuel shortages, with many gas stations experiencing supply outages due to panic buying. Georgetown Law
- Price Increases: Fuel prices surged, reaching levels not seen since 2014, as supply constraints affected consumers. Informa TechTarget
- Ransom Payment: Colonial Pipeline paid nearly $5 million in ransom to the attackers, a group identified as DarkSide, to obtain a decryption tool and restore operations.
Solutions:
- ZeroHack-N OT – Detects threats in Network traffic
- ZeroHack T OT – Decoys for luring attackers away from real systems
3. Healthcare
Key Threats:
- Medical device hijacking
- HVAC tampering in ICUs
- Ransomware on diagnostic machines
Real Attack: US Water Facility OT Hacks (2024): Hackers altered industrial controls to flash political messages.
Detailed Impact:
- Operational Impact: While the company reported no negative impact on its water or wastewater facilities and operations, customer billing and account systems were disrupted for approximately a week.
- Incident Discovery: On October 3, 2024, American Water detected unauthorized activity within its computer networks and systems, prompting immediate protective measures, including the shutdown of certain systems to investigate the breach's nature and scope
Solutions:
- ZeroHack EDR OT – Protection for diagnostic and lab systems
- ZeroHack Asset Management OT – Tracks versions of all medical OT
4. Transportation & Logistics
Key Threats:
- GPS spoofing
- Remote hijack of OT devices in airports/rail
- Malware in smart warehouse robots
Real Attack:
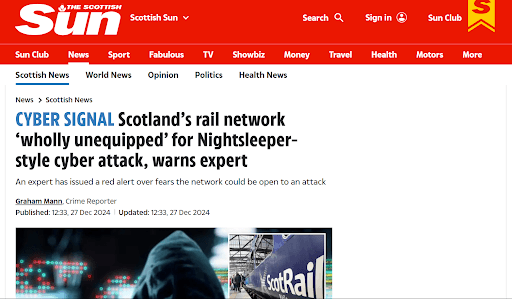
Scotland Rail Network (2024): Infrastructure deemed vulnerable; experts warned of cyber catastrophe.
Detailed Impact:
- Incident Overview: On 2024, unauthorized access to the public Wi-Fi system at several major UK train stations, including Glasgow Central and Edinburgh Waverley, led to the display of terror-related messages on station screens.
- Scope of Impact: The cyber-attack affected Wi-Fi services across 20 stations managed by Network Rail, disrupting the service for passengers and raising concerns about the security of critical rail infrastructure.
Solutions:
- ZeroHack T OT – Lures and logs attacker behavior
- ZeroHack-N OT – Detects protocol anomalies in network traffic
5. Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals
Key Threats:
- Espionage
- SCADA sabotage
- Manipulated process variables
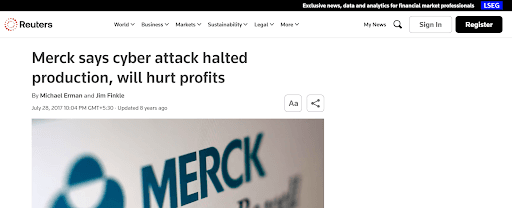
Real Attack: Merck & Co. (2017): NotPetya malware froze systems, halting production.
Detailed Impact:
- Operational Disruption: The attack led to the infection of approximately 40,000 of Merck's computers worldwide. This widespread compromise halted drug production and delayed the delivery of certain products, including key medications like Keytruda, Januvia, and Zepatier.
- Financial Impact: Merck estimated the financial damage from the attack to be around $1.7 billion, encompassing both immediate recovery costs and long-term operational disruptions.
6. Education
Key Threats:
- IoT hijacking
- Lab OT manipulation
- Research IP theft
Real Attack:
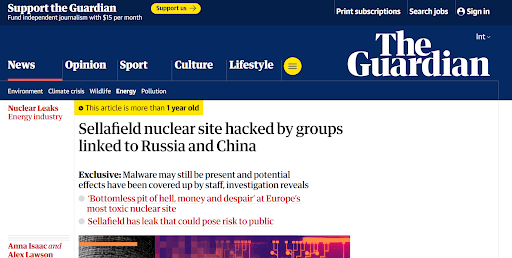
Sellafield Nuclear Research Site (UK, 2023): Hacked by suspected foreign actors.
Detailed Impact:
- Incident Overview: Sellafield's computer networks were infiltrated by cyber groups associated with Russia and China. Malware, potentially present since 2015, was discovered within the site's systems. The exact duration of the malware's presence and its status remain undetermined.
- Operational Impact: The breach raised concerns about the compromise of sensitive activities, including the management of radioactive waste, leak monitoring, and fire safety protocols.
Solutions:
- ZeroHack T OT – Detect threats in smart lab equipment with decoys
- WhizRange – Train academic and IT staff to handle targeted OT threats
Best Practices for Strengthening OT Security
1. Segment IT & OT Networks 2. Deploy OT-Specific Detection Tools 3. Implement Zero Trust for OT: “Never trust, always verify.” 4. Train Engineers with Cyber-Physical Simulations 5. Map All Assets & Monitor Continuously
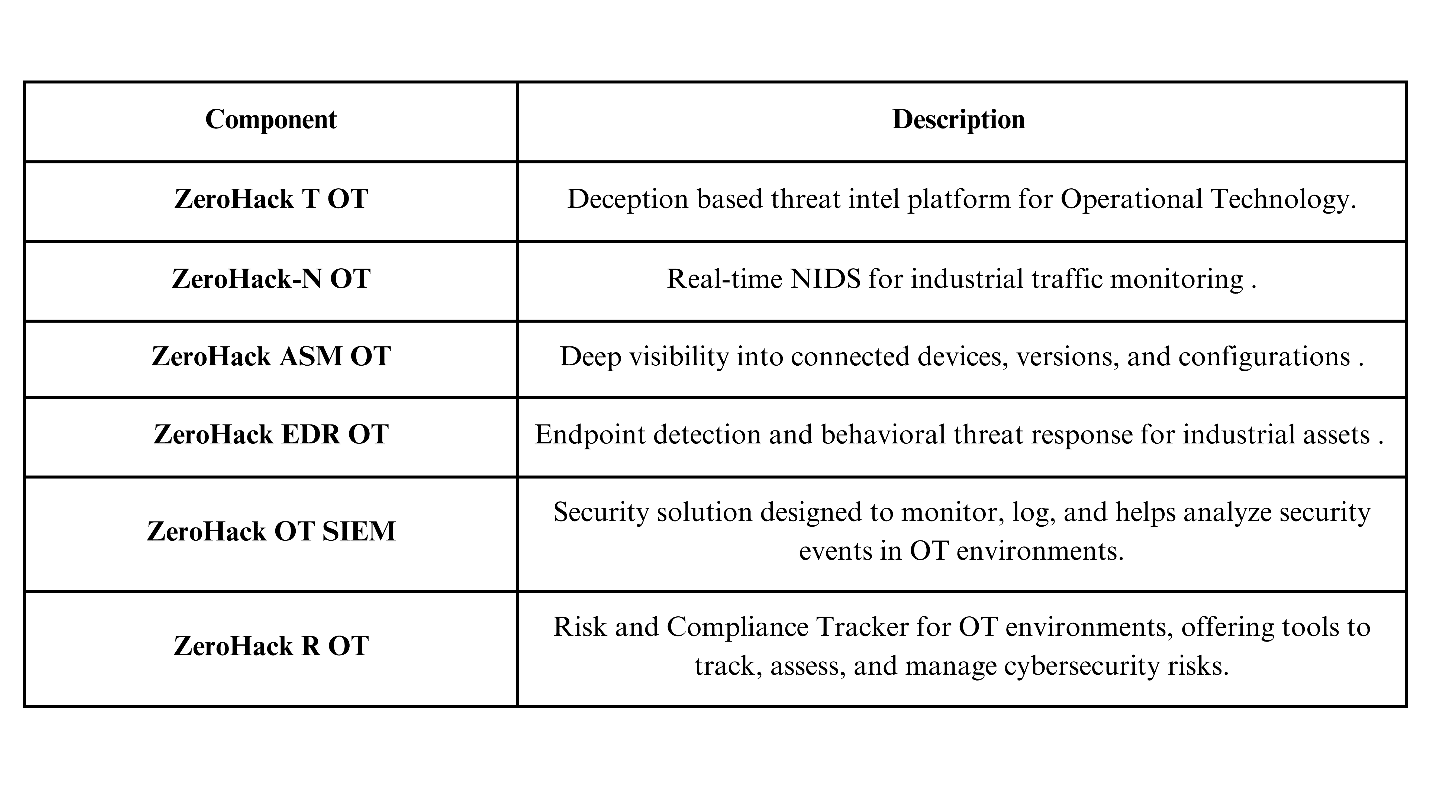
The ZeroHack XDR Suite for OT
India’s first complete OT security portfolio – built for power, precision & resilience:
💬 Let’s Start the Conversation
What are your biggest OT security concerns?
Are your OT teams ready for a real-world cyberattack?
Reach out to WhizHack Technologies today and schedule your OT Security Consultation. Together, let’s secure the future of critical infrastructure. 🚀